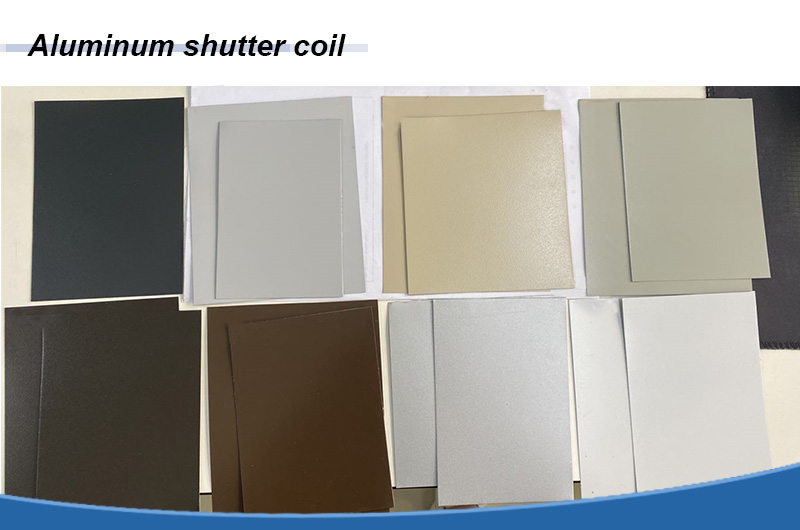
Aluminum Defects
Common aluminum sheet defects: surface oil and scratches caused by equipment mishandling or contaminated rollers.
Common aluminum coil defects: delamination, waviness, and loose winding due to poor process control or handling errors.
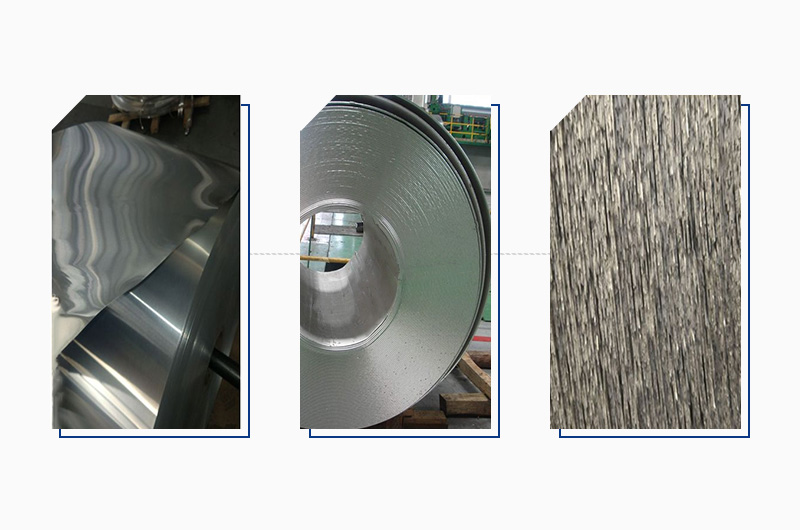
Common casting aluminum defects : surface scratches, cracks, and coarse grains resulting from unstable parameters or melting / equipment issues.
Type of Aluminum Defects
Critical Defects (Unacceptable)
- Severe structural damage: Through-holes, inclusions, overburning, etc.
- Corrosion-related damage: Corrosion, diffusion, white spots, etc.
- Structural integrity failure: Tears, cracks, etc.
- Non-compliance with mechanical properties or dimensional tolerances.
Acceptable Defects (Conditionally Acceptable)
- Surface defects (e.g., bubbles, waves, scratches) with limited area and depth.
- Minor defects (e.g., folds, non-metallic inclusions).
- Defects matching standard samples (e.g., small black spots, creases).
Other Defects (Unspecified)
Side bending, oil stains, water stains, etc., requiring evaluation against specific standards.
Surface Defects
Imprints
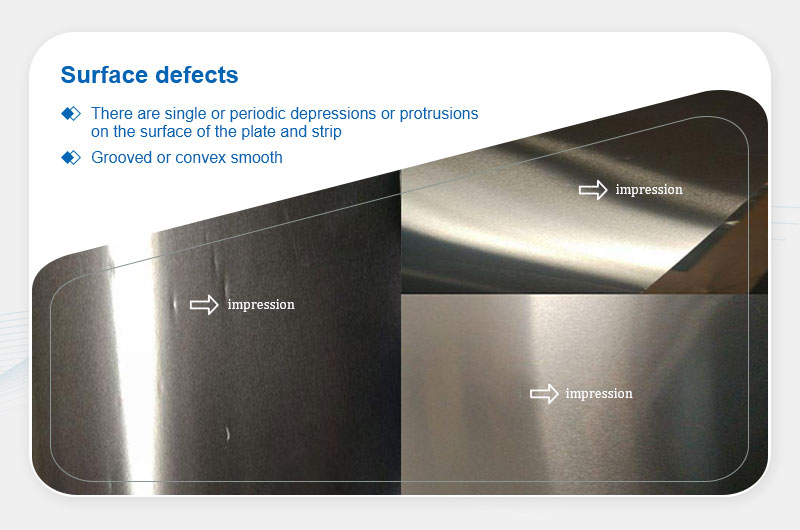
Definition: Single or periodic depressions/protrusions on the surface, smooth in texture.
Main Causes:
- Metal debris or contaminants on rolls, work rolls, or coating/oiling rollers.
- Defects or contaminants on process equipment (e.g., calenders, straighteners, feed/guide rollers).
- Dirty, uneven, or protruding coiling sleeves.
- Foreign particles adhering during coiling.
Holes
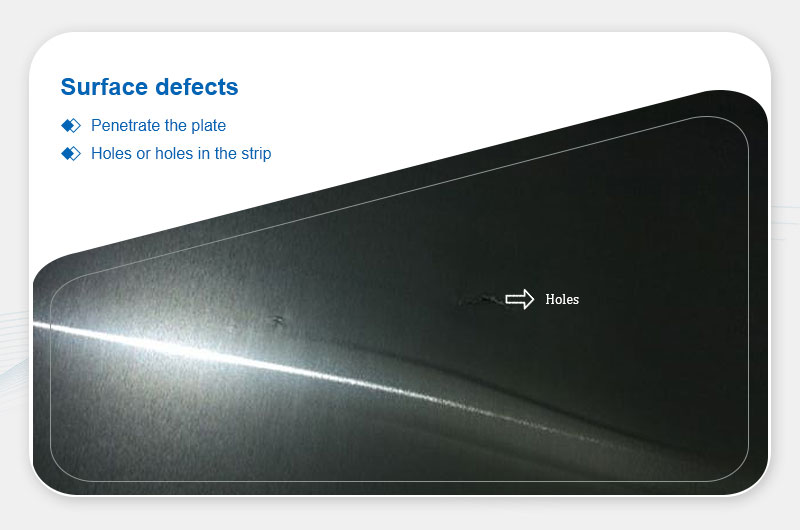
Definition: Penetrating holes or voids in the plate/strip.
Main Causes:
- Slag inclusions, scratches, or pre-existing holes in the billet before rolling.
- Detachment of embedded particles during rolling.
Non-Metallic Inclusions
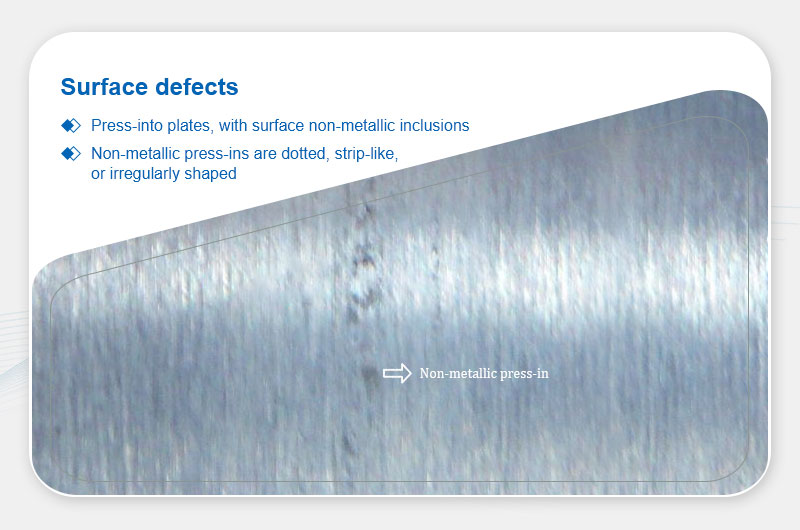
Definition: Non-metallic particles (dots, streaks, irregular shapes) embedded on the surface.
Main Causes:
- Contaminated equipment or environment.
- Dirty rolling lubricants.
- Residual non-metallic debris in billet surface scratches or oil residues.
- Foreign particles falling onto the surface during production.
Vibration Marks

Definition: Stripes perpendicular to the rolling direction, often spanning the entire width.
Main Causes:Vibrations in rolling mills, straighteners, or calenders.
Adhesion Marks
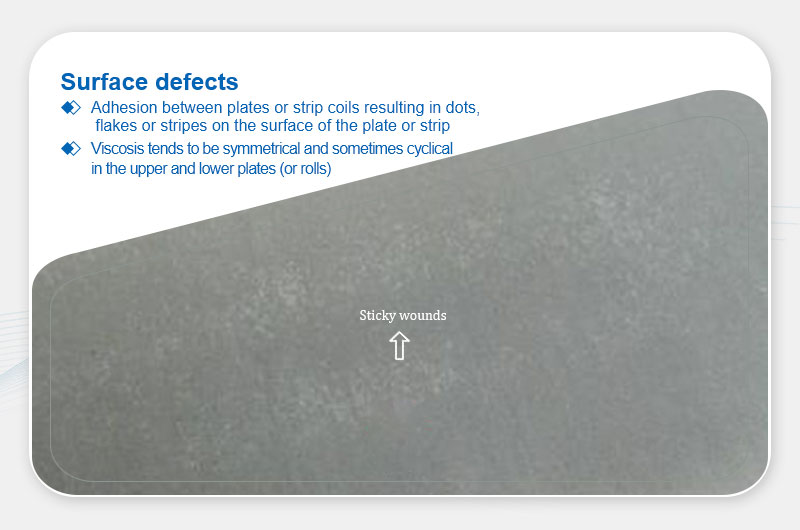
Definition: Symmetric or periodic point/streak marks from layer-to-layer adhesion.
Main Causes:
- Localized pressure on hot plates/strips.
- Excessive tension during cold rolling or coiling.
Scratches
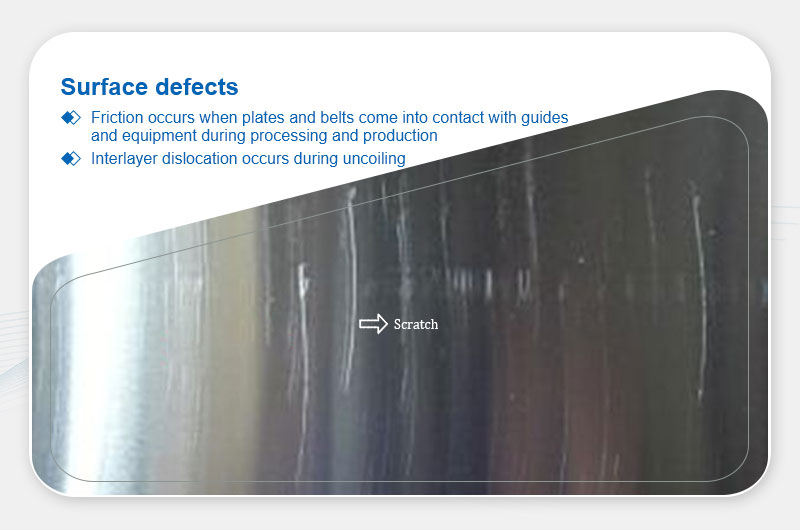
Definition: Clustered abrasions from interlayer friction or contact with equipment.
Main Causes:
- Friction with guides or equipment during processing.
- Layer misalignment during annealing or uncoiling.
- Improper handling during finishing or packaging.
Aluminum Adhesion
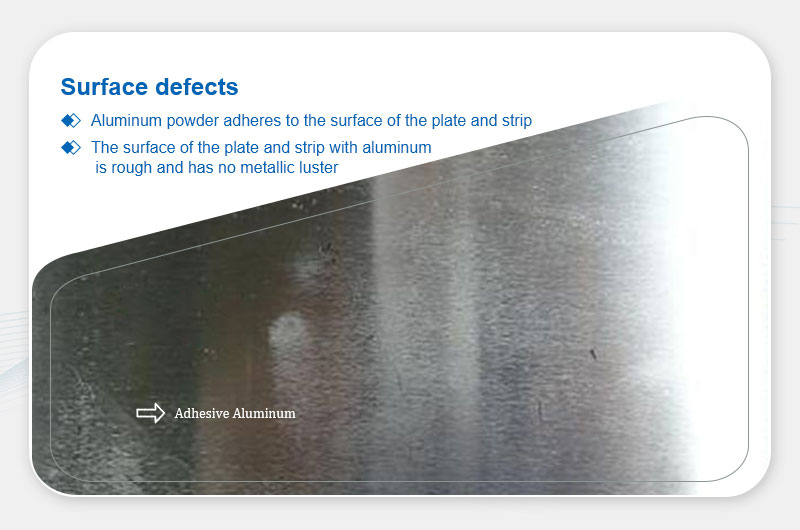
Definition: Rough, non-glossy surfaces due to adhered aluminum powder.
Main Causes:
- High billet temperature during hot rolling.
- Excessive rolling speed/pressure.
- Poor-quality lubricants.
Black Streaks

Definition: Black lines along the rolling direction.
Main Causes:
- Poor lubrication or contaminated lubricants.
- Surface scratches or dirty guides.
- Incomplete billet milling or oxide inclusion during rolling.
Oil Stains
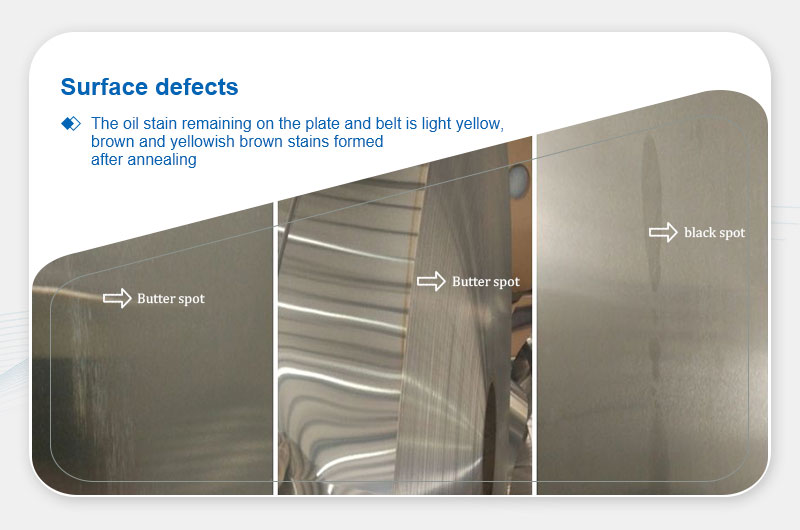
Definition: Yellow / brown residues from oil oxidation during annealing.
Main Causes:
- Unsuitable rolling oil properties.
- Incomplete oil removal before annealing.
- Contamination with high-viscosity oils.
Corrosion
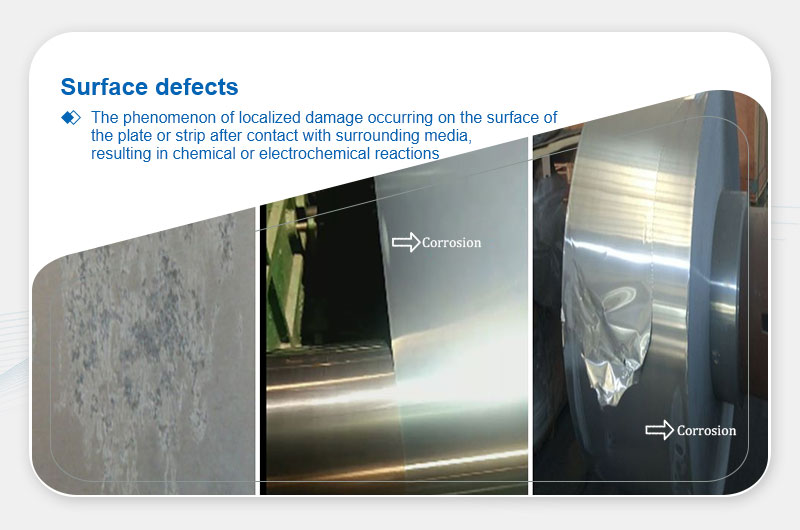
Definition: Chemical/electrochemical surface damage, often with loss of metallic luster.
Main Causes:
- Residual acids/alkalis after quenching.
- Moisture exposure during storage/transport.
- Water-contaminated lubricants or compressed air.
Bright/Dark Stripes
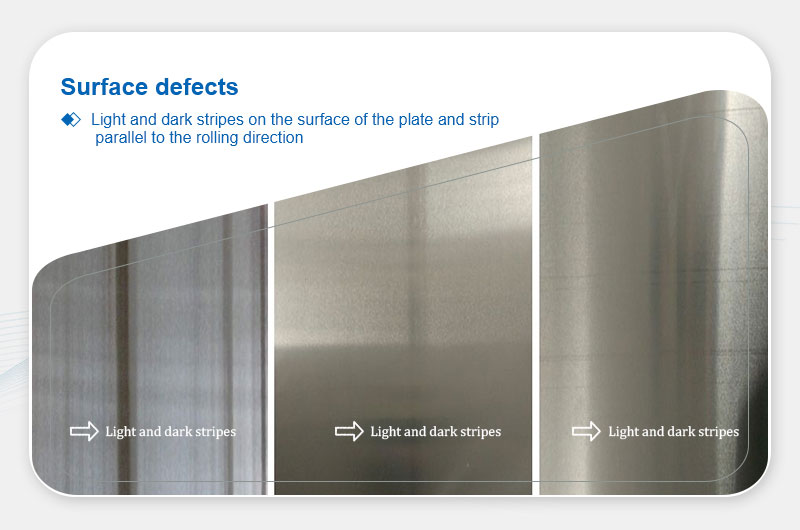
Definition: Parallel alternating glossy/matte stripes.
Main Causes:
- Poor billet surface quality or uneven lubrication.
- Roller defects or material heterogeneity.
- Rolling narrow strips before wide ones ("wide-narrow marks").
Scoring
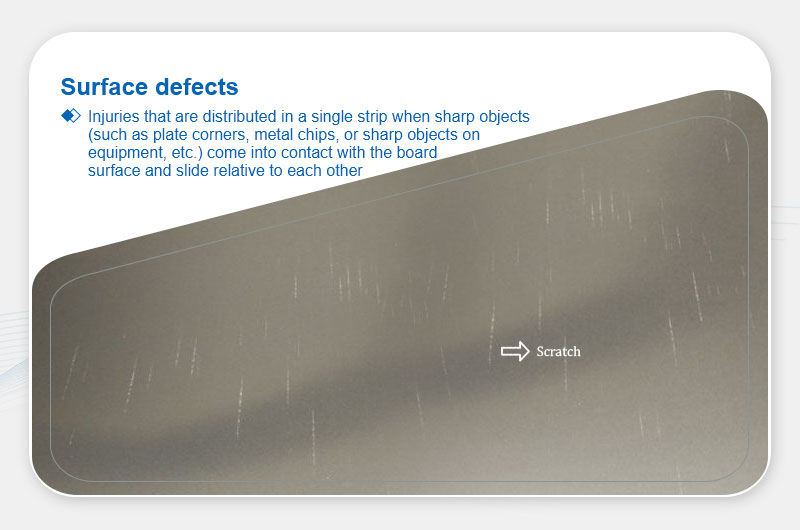
Definition: Linear scratches from sharp objects.
Main Causes:
- Aluminum buildup on hot mill guides.
- Sharp edges on cold mill equipment.
- Improper handling during finishing/packaging.
Pine-Tree Patterns/Wheel Marks
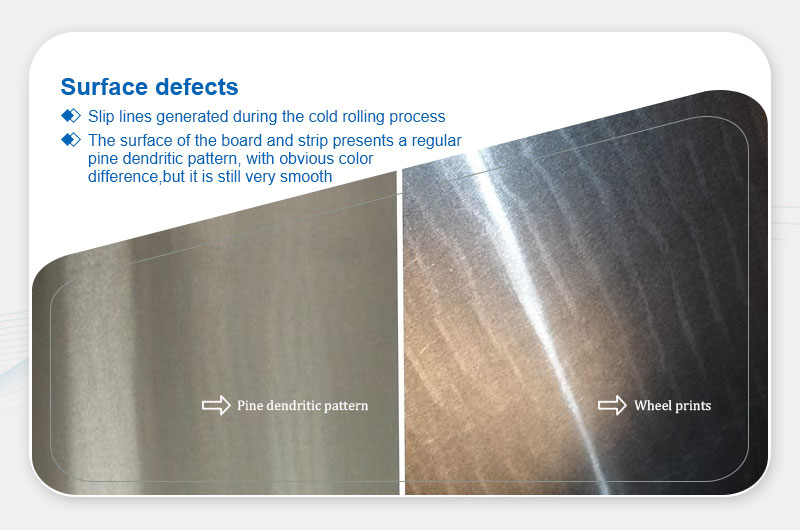
Definition: Slip lines with glossy/matte contrast, smooth to touch.
Main Causes:Poor lubrication, excessive cold rolling reduction, or low tension.
Shape Defects
Waves
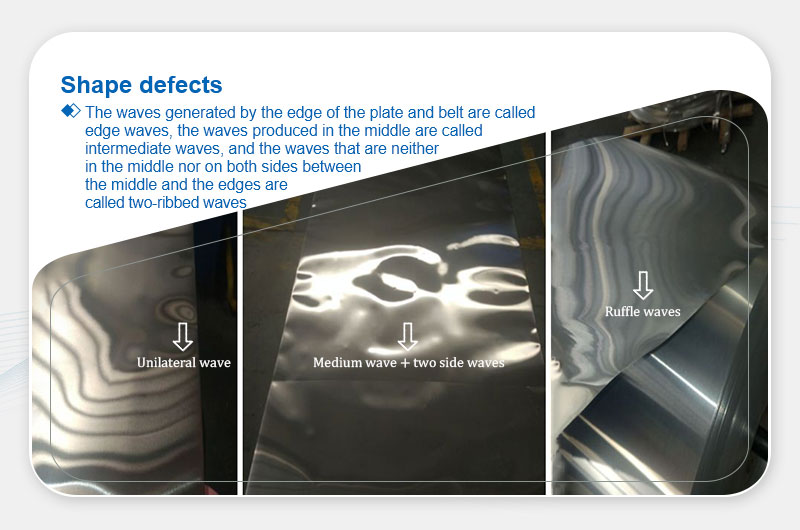
Definition: Uneven deformation causing edge, center, or localized waviness.
Main Causes:
- Uneven roll gaps or lubrication.
- Improper reduction distribution or poor incoming plate flatness.
Edge Warping

Definition: Curled edges after rolling/shearing.
Main Causes:
- Excessive rolling reduction.
- Uneven lubrication or improper shear blade alignment.
Warping and Buckling
Definition: Irregular bending from uneven stress or thermal effects.
Main Causes:Material inhomogeneity, residual stresses, temperature/humidity fluctuations.
Dimensional Defects
Thickness Deviation
Main Causes:Incorrect rolling reduction or faulty thickness gauges.
Width/Length Deviation
Main Causes:Misadjusted shearing equipment or unaccounted thermal shrinkage.
Appearance Defects
Tapered Coils
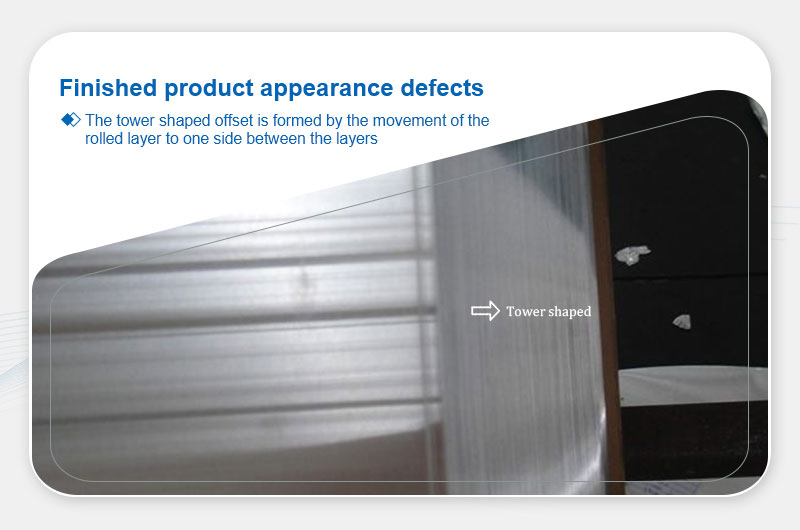
Definition: Layer misalignment forming a "tower" shape.
Main Causes:
- Poor incoming flatness or tension control.
- Faulty coiling alignment systems.
V-Shaped Defects
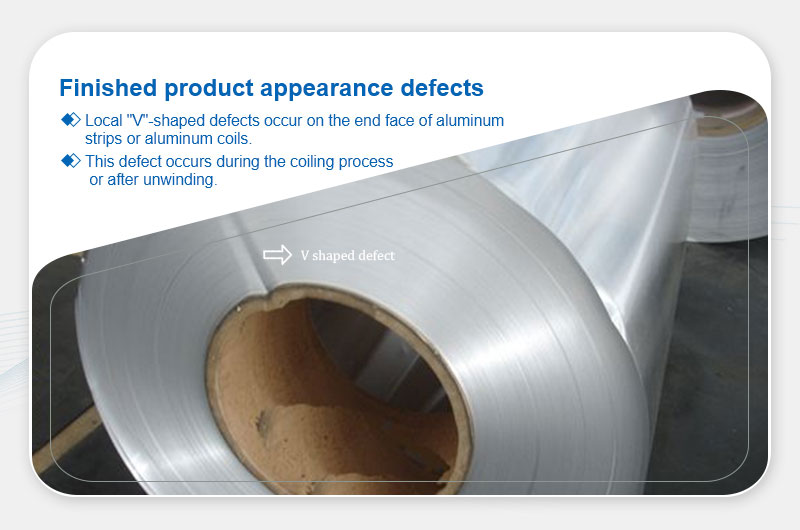
Definition: Local "V" notches on coil end faces.
Main Causes:
- Improper tension during coiling.
- Defective cores or uneven stress distribution.
Impact Damage
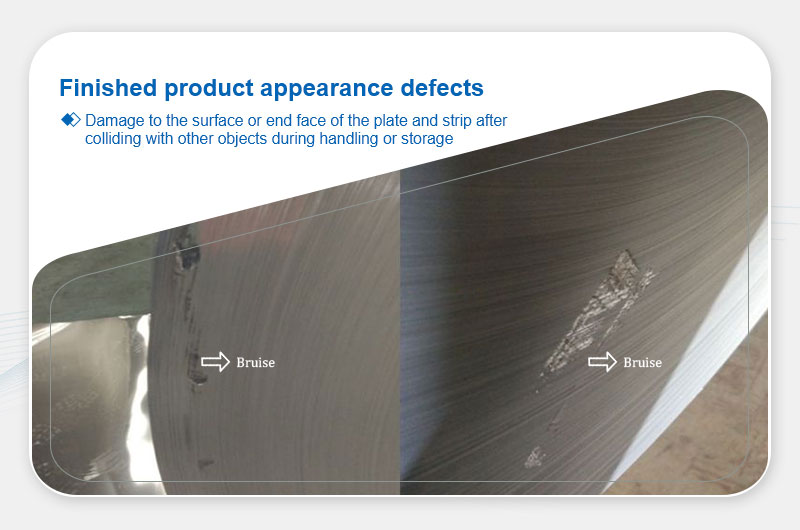
Definition: Collision-induced surface/edge damage.
Main Causes:Mishandling during transport/storage.
Collapsed Coils
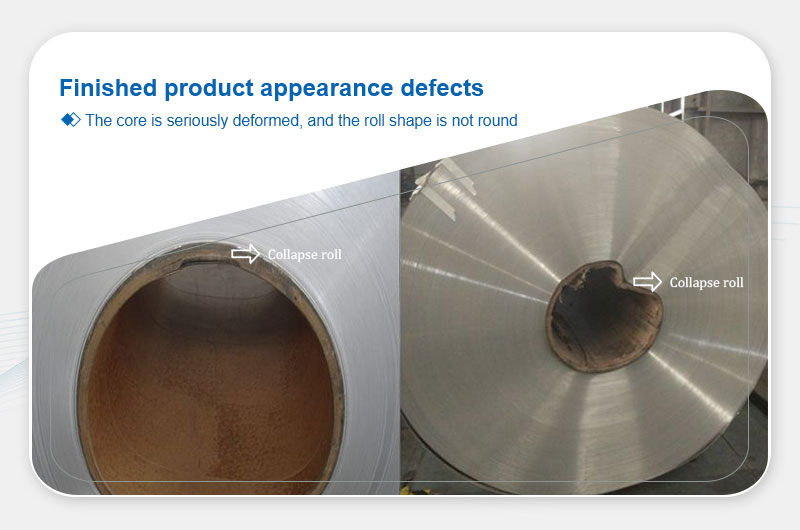
Definition: Deformed cores or non-circular coils.
Main Causes:Incorrect coiling tension, external pressure, or weak cores.
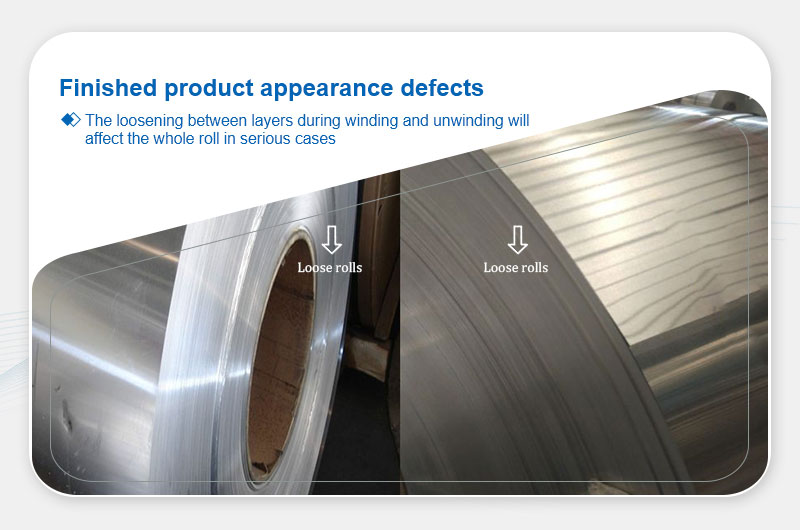
Loose Coils

Definition: Interlayer slippage during coiling/uncoiling.
Main Causes:Low tension during coiling or unsecured strapping.
Layer Misalignment
Definition: Irregular end face stacking.
Main Causes:Poor incoming flatness, uneven tension, or misaligned rollers.
Edge Defects
Burrs
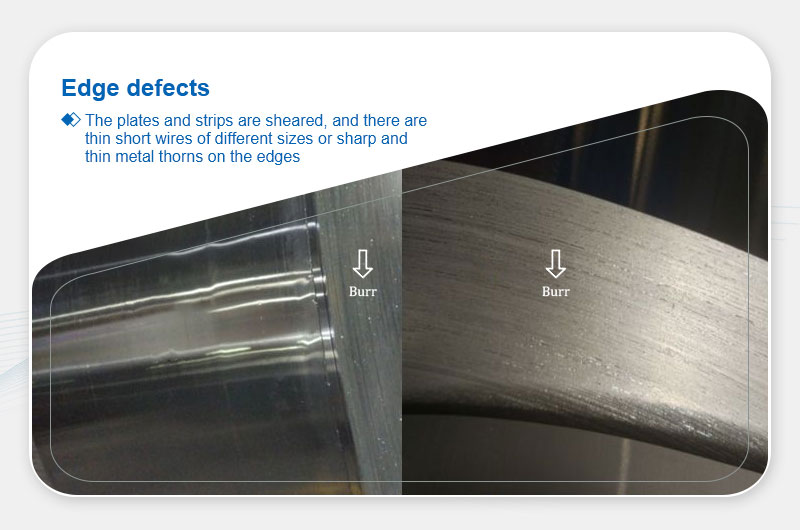
Definition: Fine metal protrusions along sheared edges.
Main Causes:Dull blades, poor lubrication, or incorrect blade settings.
Edge Cracks
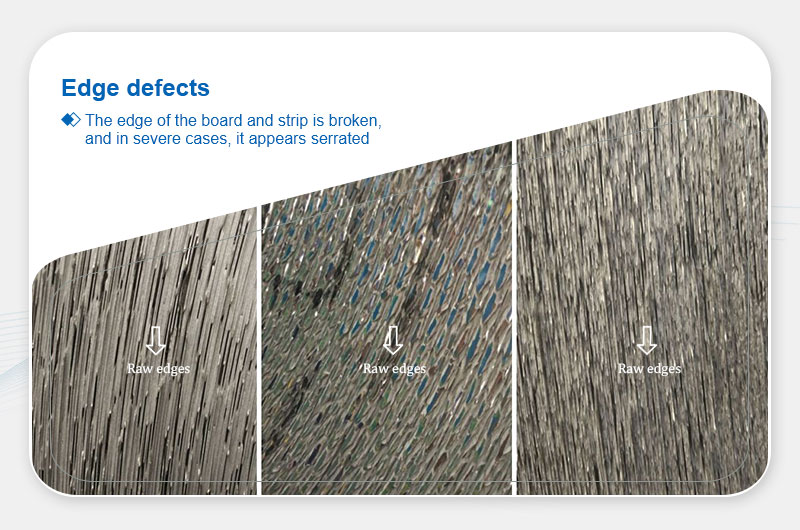
Definition: Jagged edge fractures.
Main Causes:Low billet temperature, improper annealing, or excessive reduction.
Edge Waviness
Definition: Wavy edges from uneven rolling extension.
Main Causes:Roll wear, temperature gradients, or material stress.
Edge Dents
Definition: Localized edge depressions.
Main Causes:Contact with damaged rollers or uneven cooling.
Microstructural/Performance Defects
Failed Mechanical Properties
Main Causes: Non-compliant chemical composition, improper heat treatment, or testing errors.
Overburning
Definition: Microstructural damage from excessive heating.
Main Causes:Temperature overshoots, faulty equipment, or improper furnace loading.
Casting Inclusions
Definition: Embedded foreign particles weakening the structure.
Main Causes:Impure materials, contaminated melting, or inadequate casting/rolling.
Summary
Aluminum defects arise from diverse causes but can be mitigated through optimized processes, stringent controls, and high-quality materials. Tailored solutions are essential for addressing specific defect types.





