Surface Treatment Process

What is aluminum alloy surface treatment
After the aluminum alloy surface is treated by mechanical and chemical methods, a protective layer can be formed on the surface of the aluminum alloy product.
Purpose:
- Improve durability
- Increase corrosion resistance
- Improve aesthetics
Common aluminum alloy surface treatment methods for aluminum materials include chemical treatment and physical treatment.

Chemical surface treatment
- Chromization
- Painting
- Electroplating
- Anodizing
- Electrophoresis
Mechanical (Physical) surface treatment
- Wire drawing
- Polishing
- Sandblasting
- Grinding
- Laminating
- Waxing
Surface treatment process
- Pre-treatment
- Mechanical treatment: sandblasting, shot blasting, grinding, polishing, waxing
- Chemical treatment: remove oil stains and rust, ensure that the coating has a stable state, and increase the bonding strength of the protective layer
- Film formation
- Film post-treatment
- Packaging
- Warehousing
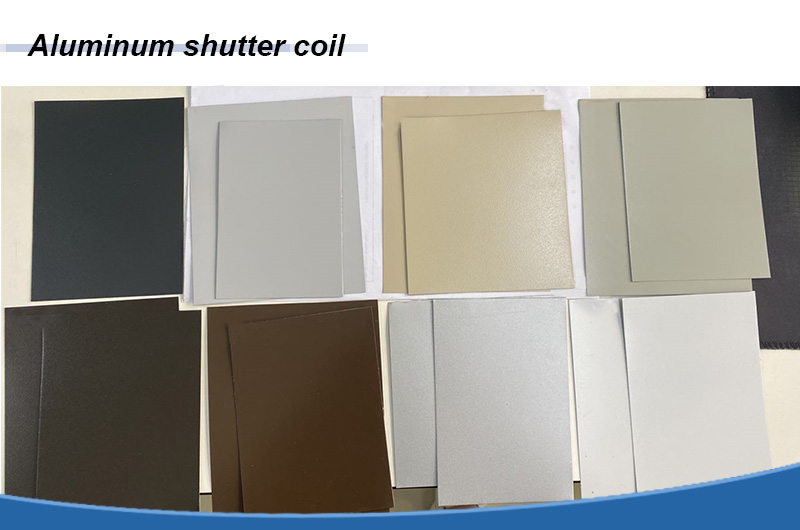
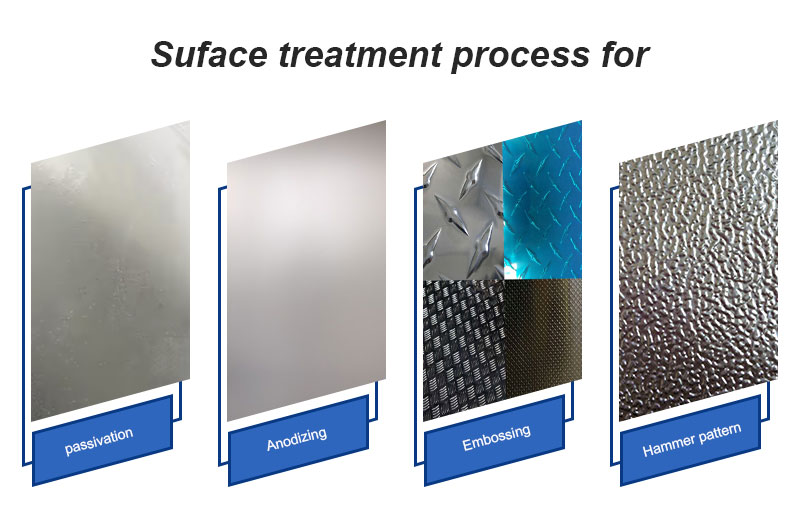
Surface treatment process for non-painted aluminum
The surface of aluminum products is not painted, and the processes are generally:
- Hammering (irregular patterns)
- Embossing (regular patterns)
- Passivation
- Anodizing
Surface treatment process for coated aluminum
Painting process type:
- Sprayed aluminum
- Pre-roller coated aluminum
Painting type:
- PE(Polyester)
- Polyurethane
- Polyamide
- Modified silicon
- Epoxy resin
- PVDF
The most commonly used coatings on the front are fluorocarbon paint (PVDF) and polyester (PE).
Among them, PVDF coated aluminum is suitable for outdoor use; PE-coated aluminum is suitable for outdoor use.
Polyester or epoxy resin coating can be selected as a protective paint coating on the back.
Surface treatment process classification
Anodizing
What is anodizing process?
Anodizing uses electrochemical principles to generate a layer of Al2O3 aluminum oxide film on the surface of aluminum. The oxide film of anodized aluminum has special characteristics such as protection, decoration, insulation, and wear resistance.
The yield level of anodizing is related to the cost of the final product. The key to improving the oxidation yield lies in the appropriate amount of oxidant, temperature and current density.
Process flow
Single or gradient anodizing process flow:
- Polishing/sandblasting/brushing
- Degreasing
- Anodizing
- Neutralization
- Dyeing
- Sealing
- Drying
Two-color anodizing process flow 1:
- Polishing/sandblasting/brushing
- Degreasing
- Masking
- First anodizing
- Second anodizing
- Sealing
- Drying
Two-color anodizing process flow 2:
- Polishing/sandblasting/brushing
- Degreasing
- First anodizing
- Laser engraving
- Second anodizing
- Sealing
- Drying
Technical features
- Improve strength
- Achieve any color except white
- Achieve nickel-free sealing
Electrophoresis
What is the electrophoresis process?
Used for stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc., it can make the product present various colors and maintain metallic luster, while enhancing surface performance and having good anti-corrosion performance.
Process Flow
- Pretreatment
- Electrophoresis
- Drying
Technical Features
Advantages:
- Rich colors.
- No metallic texture, can be used with sandblasting, polishing, brushing, etc.
- Processing in liquid environment, surface treatment of complex structures can be achieved.
- Mature process, mass production.
Disadvantages: The ability to cover defects is average, and electrophoresis of die castings requires high pretreatment.
Micro-arc oxidation
What is micro-arc oxidation process?
Micro-arc oxidation process refers to the process of applying high voltage in an electrolyte solution (generally a weak alkaline solution) to generate a ceramic surface film layer. This process is the result of the synergistic effect of physical discharge and electrochemical oxidation.
Process flow
- Pretreatment
- Hot water washing
- MAO
- Drying
Technical features
Advantages:
- Ceramic texture, dull appearance, no high-gloss products, delicate feel, anti-fingerprint;
- Wide range of substrates: Al, Ti, Zn, Zr, Mg, Nb and their alloys, etc.;
- Simple pretreatment, excellent corrosion resistance and weather resistance, and good heat dissipation performance.
Disadvantages:
- Single color
- High cost
PVD vacuum coating
What is PVD vacuum coating process?
Vacuum coating process is also called Physical vapor deposition, referred to as PVD, which is an industrial manufacturing process and a technology that mainly uses physical processes to deposit thin films.
Process flow
- Cleaning before PVD
- Vacuuming before entering the furnace
- Target washing and ion cleaning
- Coating
- Coating is completed, cooling and exiting the furnace
- Post-processing (polishing, AFP)
Technical features
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) can coat the metal surface with a high hardness and high wear resistance metal ceramic decorative coating.
Electroplating
What is the electroplating process?
Electroplating is a process that uses electrolysis to attach a layer of metal film to the surface of the metal to prevent corrosion, improve wear resistance, conductivity, reflectivity and enhance beauty.
Process flow
- Pretreatment
- Cyanide-free alkaline copper
- Cyanide-free white copper tin
- Chrome plating
Technical features
Advantages:
- High gloss coating, high-quality metal appearance
- The substrate is SUS, Al, Zn, Mg, etc., and the cost is relatively low compared to PVD
Disadvantages: poor environmental protection and greater risk of environmental pollution.
Powder spraying
What is powder spraying?
Powder coating is to spray powder coating onto the surface of workpiece with powder spraying equipment (electrostatic spraying machine). Under the action of static electricity, powder will be evenly adsorbed on the surface of workpiece to form a powder coating; the powder coating is leveled and solidified after high temperature baking to become the final coating with different effects (different types of powder coating effects).
Process flow
- mounting
- electrostatic dust removal
- spraying
- low temperature leveling
- baking
Technical features
- Rich colors, high gloss and matte optional;
- Low cost, suitable for architectural furniture products and heat sink shells, etc.;
- High utilization rate, 100% utilization, environmental protection;
- Strong ability to conceal defects;
- Can imitate wood grain effect.
Brushed
What is brushed process?
Brushed process is a surface treatment method that forms lines on the surface of the workpiece by grinding the product to achieve decorative effect. According to the different patterns of brushed aluminum, it can be divided into:
- Linear brushing
- Random brushing
- Wavy brushing
- Spiral Brushing
- Thread drawing
- Cross brushing
Technical features
Wire drawing can make the metal surface obtain non-mirror-like metallic luster, and wire drawing can also eliminate minor flaws on the metal surface.
Sandblasting
What is sandblasting?
Sandblasting is a process that uses compressed air as a power to form a high-speed jet beam to spray the material at high speed onto the surface of the aluminum product to be processed, so that the aluminum surface can obtain a certain degree of cleanliness and different roughness.
Technical features
- Achieve different reflections or matte.
- Clean the tiny burrs on the surface of the workpiece and make the surface of the workpiece smoother
- Remove dirt and improve the finish of the workpiece,
Polishing
Polishing is a modification process of the workpiece surface using flexible polishing tools and abrasive particles or other polishing media.
According to different polishing processes, it can be divided into:
- Rough polishing (basic polishing process)
- Medium polishing (finishing process)
- Fine polishing (glazing process)
Choosing a suitable polishing wheel can achieve the best polishing effect and improve polishing efficiency.
Improve the dimensional accuracy or geometric shape accuracy of the workpiece, obtain a smooth surface or mirror gloss, and also eliminate gloss.
Etching
What is the etching process?
Etching process usually refers to etching, also known as photochemical etching, which refers to the removal of the protective film of the etching area after exposure and development, and contact with chemical solution during etching to achieve the effect of dissolving and corroding, forming a concave-convex or hollow-out molding effect.
Process flow
Exposure method:
- The project will prepare the material size according to the drawing
- Material preparation
- Material cleaning
- Drying
- Filming or coating
- Drying
- Exposure
- Development
- Drying
- Etching
- Demolding
Screen printing method:
- Cutting
- Cleaning the plate (stainless steel and other metal materials)
- Screen printing
- Etching
- Demolding
Technical features
Advantages:
- Fine processing of metal surface can be performed
- Special effects are given to the metal surface
Disadvantages: Most of the corrosive liquids (acids, alkalis, etc.) used in etching are harmful to the environment





